
Did You Know?
Lung cancer accounts for nearly 1 in 5 of all cancer deaths.
Smoking is the greatest risk factor for lung cancer, but not all people who get lung cancer smoke.
No matter what your age or how long you've smoked, quitting will lower your risk of lung cancer.
Lung Cancer Screening
You should talk with your doctor about getting screened if:
You are 50-80 years old.
Medicare and Medicaid cover the cost of the test for people 50-77 years old. Because of that, some hospitals may only provide screening for people 50-77 years old.
- You smoke cigarettes or quit in the last 15 years.
You have smoked at least 20 pack-years
This is the equivalent of 1 pack of cigarettes per day for 20 years. To figure out your pack-years, click here.
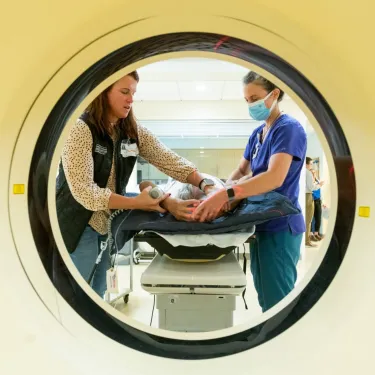
Lung cancer screening looks for lung cancer before you have symptoms. It involves a quick and painless CT scan (a special type of x-ray) that takes multiple pictures to help doctors get a good look at your lungs.
Not all lung cancers can be prevented, but you may be able to lower your risk for lung cancer by changing the risk factors that you can control. Lung Cancer Prevention
Lung Cancer Overview
What is Lung Cancer?
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. When this growth starts in the lungs, it is called lung cancer. There are two main types of lung cancer: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). 80-85% of lung cancers are NSCLC, including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. These are grouped together as NSCLC because their treatment and outlook is similar. 10-15% of lung cancers are SCLC, which tend to grow and spread faster than NSCLC.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common lung cancer symptoms include:
- A cough that does not go away or gets worse
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored spit or phlegm
- Chest pain that is often worse with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing
- Hoarseness
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling tired or weak
- Infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia that don't go away or keep coming back
- New onset of wheezing
Signs and symptoms of lung cancer that has spread:
- Bone pain
- Nervous system changes (including headache, weakness or numbness of limbs, dizziness, balance problems, or seizures)
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Swelling of lymph nodes
Source: American Cancer Society, 2025
Risk Factors
What is a risk factor? A risk factor is anything that increases your chances of getting a disease, such as cancer.
Potentially modifiable risk factors for lung cancer include:
- Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke
- Exposure to radon (learn more here)
- Exposure to asbestos
- Exposure to other cancer-causing agents, including diesel exhaust
Risk factors you cannot change include:
- Personal or family history of lung cancer
Factors with uncertain or unproven effects on lung cancer risk include:
- Smoking marijuana
- Smoking e-cigarettes
Source: American Cancer Society, 2025
Related stories

When Lung Screening Saves Lives: One Patient’s Story
Lung Cancer in Our Catchment Area (VT and Northern NY)
Incidence
Age-adjusted incidence for lung cancer ranges from 48 per 100,000 in Windsor County, VT to 92 per 100,000 in Clinton County, NY.
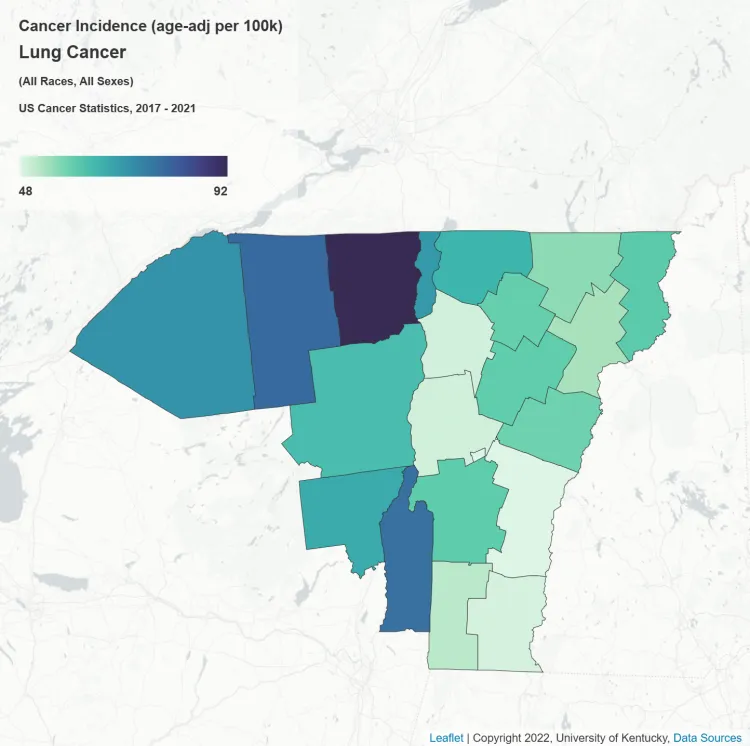
Source: Cancer InFocus, 2025
Mortality
Age-adjusted mortality from lung cancer ranges from 27 per 100,000 in Windsor County, VT to 45 per 100,000 in Franklin County, NY.
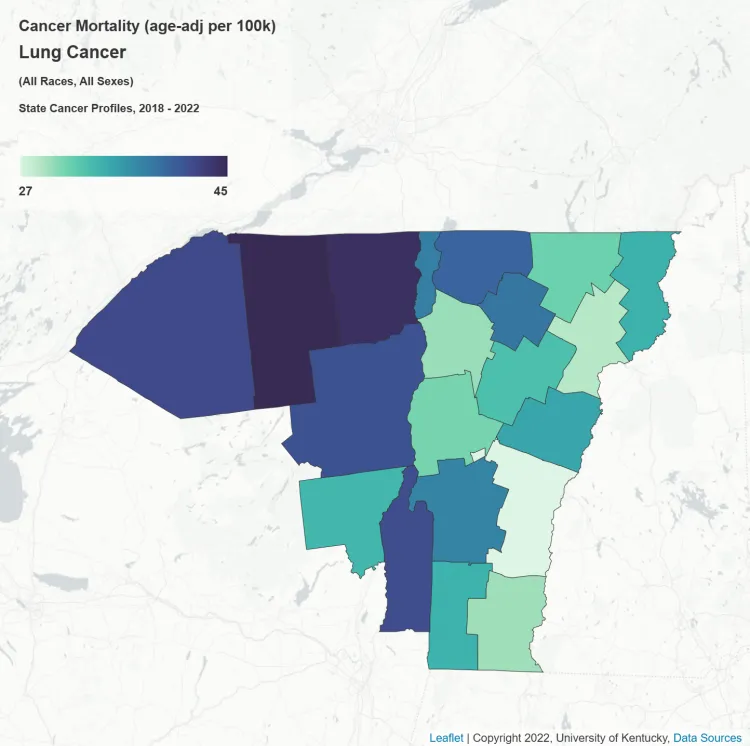
Source: Cancer InFocus, 2025
Clinical advisor: Beth Zigmund, MD, Director of Lung Cancer Screening, University of Vermont Medical Center
For questions about the lung cancer program, please contact the Community Outreach and Engagement Team at COE@med.uvm.edu





