Outlook offers significant configuration options for handling incoming messages. In this guide, you will find instructions on blocking senders, marking senders as safe, setting up forwarding, and creating or removing inbox rules.
In addition to configuring the way your mail client filters emails, you may also follow the steps detailed in the following guide to report an email as malicious, or to report a false positive or false negative: https://www.uvm.edu/it/kb/article/proofpoint.
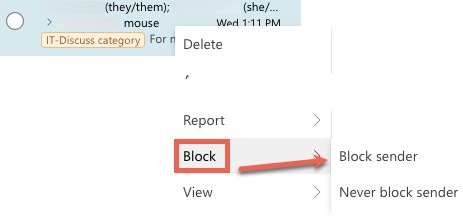
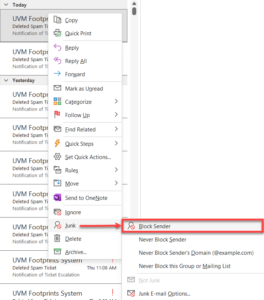
Blocking a Sender
If spam messages appear in your inbox, you can block the sender or domain. This is a quick and straightforward process, but it has limited configuration options. If you require a more complex rule, please see Creating an Inbox Rule below.
Outlook Online
Outlook for Microsoft 365
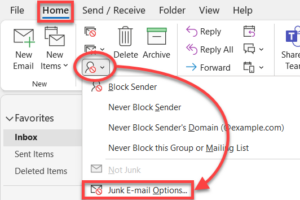
Managing Blocked Senders
Outlook Online
- Click the Gear icon near the upper-right corner to open the Settings menu.

- Within the Mail tab on the left side, select Junk email.
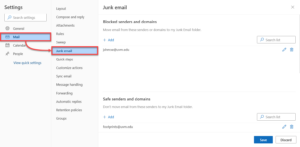
- To block a sender or domain, click + Add under Blocked senders and domains, type in the address or domain name you wish to block, and then press the Enter key.
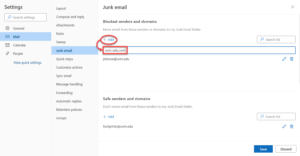
- Click Save at the bottom of the window to confirm your changes.
Outlook for Microsoft 365
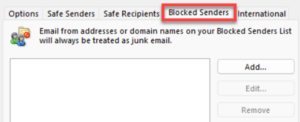
Marking a Sender as Safe
Conversely, if you notice legitimate emails ending up in your Junk Email folder in Outlook, you can mark the sender of these emails as safe.
Outlook Online
- Click the Gear icon near the upper-right corner to open the Settings menu.

- Within the Mail tab on the left side, select Junk email.

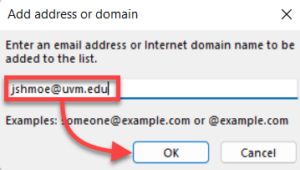
- To mark a sender or domain as safe, click + Add under Safe senders and domains, type in the address or domain name you wish to mark as safe, and then press the Enter key.
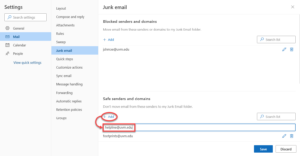
- Click Save at the bottom of the window to confirm your changes.
Outlook for Microsoft 365
Forwarding
Outlook Online
- Log in to Outlook Online.
- Click the Gear icon near the upper-right corner to open the Settings menu.

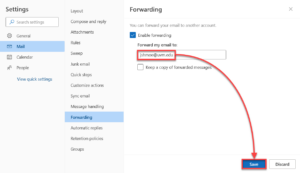
- Within the Mail tab on the left side, select Forwarding, and then check the box marked Enable forwarding.
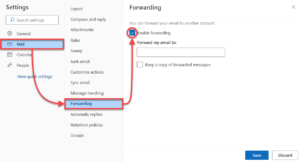
- Enter the address you would like to forward your email to, and then click Save.
Creating an Inbox Rule
Inbox rules can automatically move mail from your inbox to a selected folder, categorize messages by custom criteria, and much more.
Outlook Online
- Click the Gear icon near the upper-right corner to open the Settings menu.

- Within the Mail tab on the left side, select Rules, and then click + Add new rule.
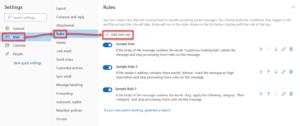
- Enter a name for your rule.
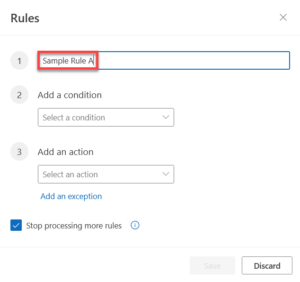
- Choose a trigger condition, and then choose an action that should take place when the condition is met.
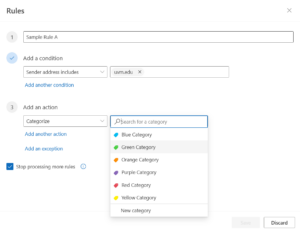
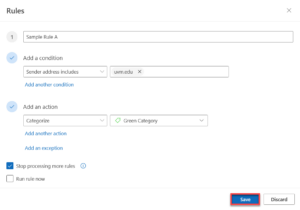
- When you’re done, click Save.
Outlook for Microsoft 365
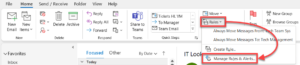
- Select the Home tab.
- Expand the Rules drop-down and click Manage Rules & Alerts.
- In the Rules and Alerts window, click New Rule.
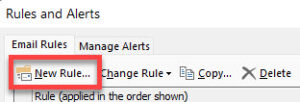
- Some popular rules have templates you can select; otherwise, select one of the blank rules at the bottom and click Next.
- On the first page of the Rules Wizard, select any conditions that you would like to trigger the rule, make any necessary edits, and then click Next.
- On the next page, select any actions that you would like to perform when the rule triggers, make any necessary edits, and then click Next.
- On the third page, select any exceptions to the rule that you would like to add (if any), make any necessary edits, and then click Next.
- On the final page, specify a descriptive name for the rule, ensure Turn on this rule is checked, and then click Finish.
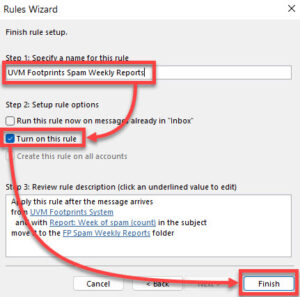
You should now see the rule with a check mark next to it in the list of Email Rules.
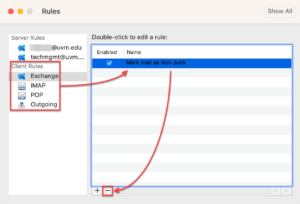
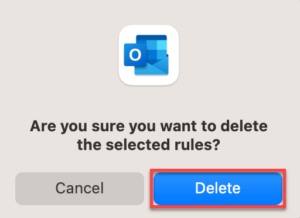
Removing Client-Side Rules
In Outlook (and other email clients), it’s possible to create rules that only affect the client on which they are configured. This typically happens if you try to create a rule that can’t be processed by Exchange, such as one that prints an email. If you try to create a rule like this, Outlook will warn you that the rule will be client-side only, and it will ask you to confirm.
Client-side rules will not carry over to a new computer, device, alternate email client, or Outlook Online. Additionally, it’s difficult to troubleshoot mailbox issues when IT does not have a complete view of the rules impacting your account. Thus, it’s highly recommended to use only server-side rules.