Center for Resilient Energy & Autonomous Technologies in Engineering (CREATE)

CREATE is a newly established research center focused on advancing the next generation of energy and autonomous technologies. The center is driven by the rapid changes in today’s power and energy systems, spurred by the aggressive decarbonization and electrification policies in Vermont and beyond. Concurrently, the development of new software algorithms in autonomy holds the potential to greatly enhance the dynamic capabilities, performance, and efficiency of engineered systems. At the intersection of these two focus areas of the proposed center (Power/Energy and Autonomy/Controls), CREATE develops technologies that enable resilient and responsive power and energy systems, as well as data-driven feedback control solutions. CREATE seeks to scale the impact of our research efforts in these focus areas to advance human knowledge and solve critical problems facing our society today.
Center for Biomedical Innovation (CBI)

UVM’s Center for Biomedical Innovation (CBI) is an internationally recognized hub for design, development, and testing of biomedical devices and systems with a focus on rural healthcare.
The center supports and trains inventors, entrepreneurs, and business leaders who will bring advanced biomedical technologies to the people of Vermont and the world. The CBI brings together students, faculty, and industry through shared programming and an interactive space for applied research, technology development, and education.
Glass Brain Lab

The Glass Brain Lab’s mission is to break human neuroimaging out of the lab using machine learning and emerging technologies like mobile EEG, fMRI functional connectivity, and natural language processing. By understanding the brain as it operates in real life, we can pave the way for devices that detect problematic brain states in real-time and provide help or support, a sort of pacemaker for the brain. Sample projects include:
- Mindless Reading: Decode brain & eye signals during reading to predict comprehension.
- The Aha Moment: Detect the orienting of attention in real-life scenarios to shed light on ADHD.
- Automated Therapy Labeling: Detect exposure therapy techniques to see what works.
Website: www.uvm.edu/~brainlab/
Contact: Dr. David Jangraw
Sensor Network and Wireless Lab

The work conducted in UVM’s Sensor Network and Wireless Lab is motivated by the prospect of better understanding our natural and built environments through the use of wireless systems. The most significant contributions of the lab to date are as follows…
- Recognizing the existence of, developing models for, and characterizing hyper-Rayleigh channels that can be found in cluttered environments in which wireless systems and IoT devices are deployed.
- Developing and characterizing new tripolar antenna systems to mitigate 3D depolarization seen in cluttered environments.
- Developing new automaton-based strategies so that devices maintain system level quality of service while at the same time reducing the overhead for operation.
The work has been funded by NSF, DoE and DoT and resulted in over 30 former graduate students, more than 150 peer-reviewed publications, nine patents, and one start up.
Contact: Jeff Frolik
Controls@UVM Lab
Our primary research interests lie in the areas of dynamical systems, control theory, and autonomy. The group is currently involved in collaborative research aiming to develop constraint-aware and uncertainty-aware control algorithms with applications in automotive, aerospace, and power systems. Additionally, we are interested in developing data-driven control methods for constrained control systems, as well as control and fault detection methods for aerial drones.
Current Projects include:
- Coordination and control of satellite swarms. Sponsor: NASA
- Control and constraint management of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. Sponsor: Ford Motor Company
- Real time control of distribution grids with uncertain distributed energy resources. Sponsor: US DoE and NIST
Contact: Hamid Ossareh
Biomedical Nanotechnology and Biomaterials Lab
Research in the Biomedical Nanotechnology and Biomaterials Lab focuses on several interrelated topics--biomaterials, molecular imaging, drug delivery, and nanotoxicity—in an effort to better diagnose and treat disease. Our lab uses materials at the nano and macroscopic level that are designed to interact favorably with the human body to achieve a desired outcome. For example, we design and make nanoparticles loaded with various active agents to aid in diagnosing inflammatory diseases and infections using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). We also have developed a nanoparticle capable of delivering an enzyme that both prevents and eliminates difficult-to-treat infections called biofilms. When used to treat in vitro or in vivo infections, this technology is 100,000 times more effective than conventional therapies. We are currently working on an enzyme-free biomaterial approach to use as a wound dressing to prevent and treat biofilm infections.
Website: https://site.uvm.edu/bnb/
Contact: Amber Doiron
Musculoskeletal Imaging and Orthopaedic Biomechanics (MIOB) Lab
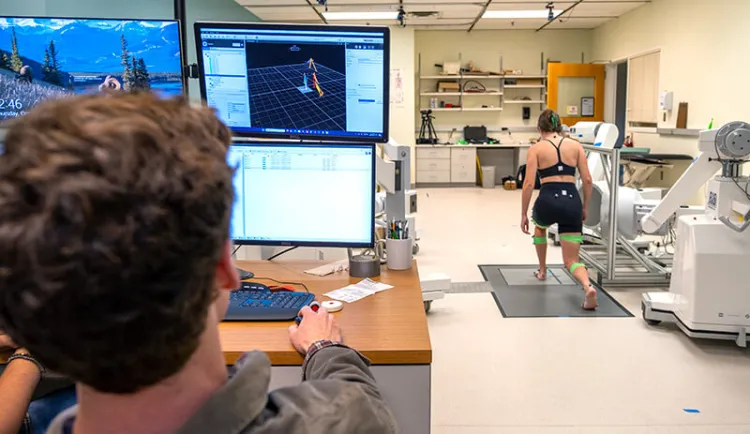

The overarching goal of the Musculoskeletal Imaging and Orthopaedic Biomechanics (MIOB) Laboratory is to improve human health and performance for those who suffer from musculoskeletal and orthopaedic conditions. Our approaches span experimental and computational methods. We use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize disease and quantify anatomy, and we image bone motion directly with dynamic x-ray. Our computational studies combine patient-specific MR-based models with dynamic motion measurements to estimate internal tissue mechanics of orthopaedic tissues. Overall, the experimental and computational methods employed by the MIOB lab aim to improve health outcomes and reduce burdens imposed on patients and our healthcare system.
Website: www.uvm.edu/~nfiorent/
Contact: Nic Fiorentino
CORE Systems Lab

The CORE (Control and Optimization of Responsive Energy) Systems Lab's goal is to advance our fundamental understanding of how power and energy systems can actively and reliably respond to changing market and grid conditions and enable a clean energy future. Towards this objective, our group seeks to develop impactful grid-aware control and optimization algorithms that coordinate distributed, networked grid and energy resources. Our group's work, thus, investigates modeling and control of fleets of distributed energy resources (DERs) as virtual energy storage (VES), optimization of DERs in transmission and distribution systems, and real-time validation of algorithms in a practical context. Recent/ongoing projects include:
- DOE ARPA-E (NODES): large-scale coordination of DERs under packetized energy management in T&D systems (Partners: Michigan Tech., Florida International Uni, GMP, VELCO, Packetized Energy, and CEPC)
- DOE SETO (ENERGISE): hierarchical robust control and optimization of DERs in distribution systems with very high penetration of solar PV (Partners: PNNL, Johns Hopkins Uni, O&R, , and NIST)
Website: madsalma.github.io/
Contact: Dr. Mads Almassalkhi
Autonomous and Intelligent systems Research Laboratory (AIRLab)

The Autonomous and Intelligent systems Research Laboratory (AIRLab) has as its primary objective contributing to the development and deployment of autonomy technologies. Particularly, the laboratory is at the crossroads of the fields of systems and control engineering, signal processing, and estimation. The lab is co-directed by Prof. Luis Duffaut and Prof. Hamid Ossareh from EBE. Our team currently works in projects related to planning and formation of autonomous systems, localization and mapping, fault tolerant state estimation, free model learning technologies for navigation in harsh environments, constraint management of autonomous systems, and control of unmanned vehicles such as UAVs, among others. The research performed by our members is expected to make a significant contribution to science and society at large in that our research is highly adaptive to other engineering disciplines. Moreover, graduate and undergraduate students at the AIRLab benefit from acquiring a broad set of engineering skills, which prepares them to enter a constantly evolving workforce.
Contact: Luis Duffaut
High-Performance Circuits and Systems (HP-CAS) Lab

High-Performance Circuits and Systems (HP-CAS) Laboratory: The HP-CAS Lab investigates innovative high performance electronic circuits and systems design, test and applications. The research spans analysis, modeling, design, simulation and validation of analog, mixed signal, RF and microwave circuits and systems. We also explore novel applications in remote sensing, wireless communications and reconfigurable computing. Currently HP-CAS Lab is performing active research on the following subjects:
- Ultrawide bandwidth (UWB) radar for subsurface sensing and non-destructive evaluation (NDE)
- Adaptive communication transceiver integrated circuit design using CMOS/SiGe technology
- Joint communication and radar design
- Multi-modal sensing circuit design
- Integrated circuit security with a self-destructing capability
HP-CAS research has been supported by multiple funding agencies, including NSF, NASA, DoD, NIST, DoT, Vermont Agency of Transportation (VTrans), IBM, etc. Students graduated from HP-CAS Lab joined IBM, Global Foundries, Qualcomm, Delphi Automotive, Intel, Texas Instruments (TI), Mentor Graphics, Galen Healthcare Solutions, OmniVision Technologies and others.
Website: https://sites.google.com/view/txia-uvm
Contact: Tian Xia
Cipolla Lab

The primary goal of our research is to understand the structure and function of the cerebral circulation under normal and pathological conditions and how cerebrovascular dysfunction can promote brain injury during ischemic stroke and seizure. First, we study how the cerebrovasculature responds functionally during both ischemia to limit collateral perfusion and du ring reperfusion to promote blood-brain barrier disruption and impair perfusion. Second, we study how pregnancy and preeclampsia affect the blood-brain barrier and cerebral blood flow autoregulation in ways that promote the neurological complications of preeclampsia, including seizure (eclampsia). We have determined mechanisms by which circulating factors in pregnancy and preeclampsia cause edema formation and promote seizure, including VEGF and oxidized LDL. The Cipolla laboratory has unique expertise in vascular biology, reproductive sciences and neuroscience that has provided novel insight into both the stroke and eclampsia fields.
Website: www.med.uvm.edu/neuro/cipolla_lab/
Contact: Marilyn Cipolla
Microbiome Metabolic Modeling Lab

The Microbiome Metabolic Modeling (“M-cubed”) lab develops computational tools to better understand microbial ecosystems. Microbial organisms are ubiquitous in nature, forming complex ecosystems that influence human health and environmental processes. Our goal is to improve quantitative understanding of these microbial systems to leverage control points of environmental processes and design treatments for human diseases. We focus primarily on metabolism, and genome-scale metabolic models, through which we can link genomic data to multi-scale computational models of microbial physiology. Current research projects in the lab relate to general improvement of genome-scale metabolic model accuracy through experimental validation, and development of dynamic computational models of the infant gut microbiome.
Contact: David Bernstein