Skip to main content
Interpreting Nuclear Medicine Studies
- Most images are in gray scale and have poor anatomic detail, as seen in the image on the right.
- Radioactive isotopes are injected or ingested, and the patient is scanned.
- Photons hitting the detectors are counted and converted into images.
- Black areas represent higher counts, indicating increased radiotracer uptake or "hot" spots.
- White areas represent lower counts, indicating low uptake or "cold" spots.
- In some studies, (such as PET scans) these images can be combined with standard CT scans to create a "fused" image.
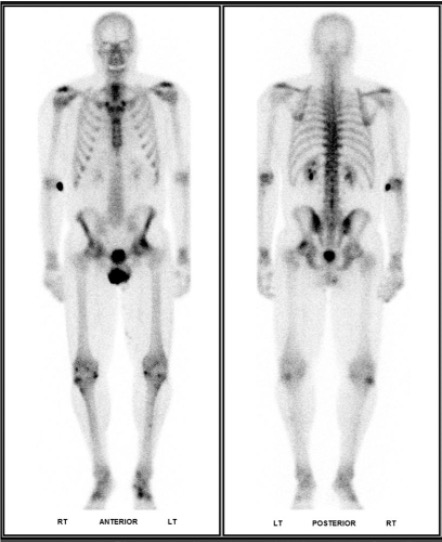 Normal bone scan.
Normal bone scan.
Intro to Bone Scans
- Radiotracer- Technetium 99m MDP.
- "Hot" uptake at sites of active turnover
- Kidneys should be faintly visible. If there is sufficiently strong uptake in the bones, the kidneys will not be seen- this is called a superscan
- Symmetry is your friend!
- Focal uptake in the joints most likely represent degenerative changes.
- If you are not sure- correlate
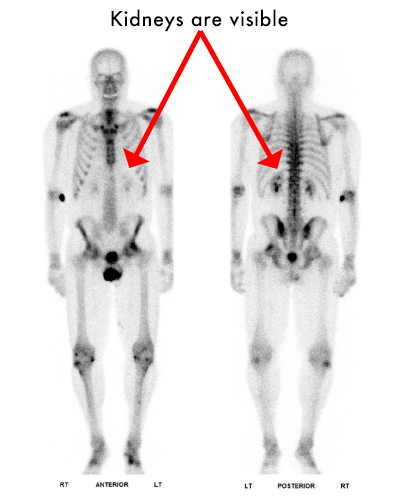 Normal bone scan anterior (left) and posterior (right).
Normal bone scan anterior (left) and posterior (right).

