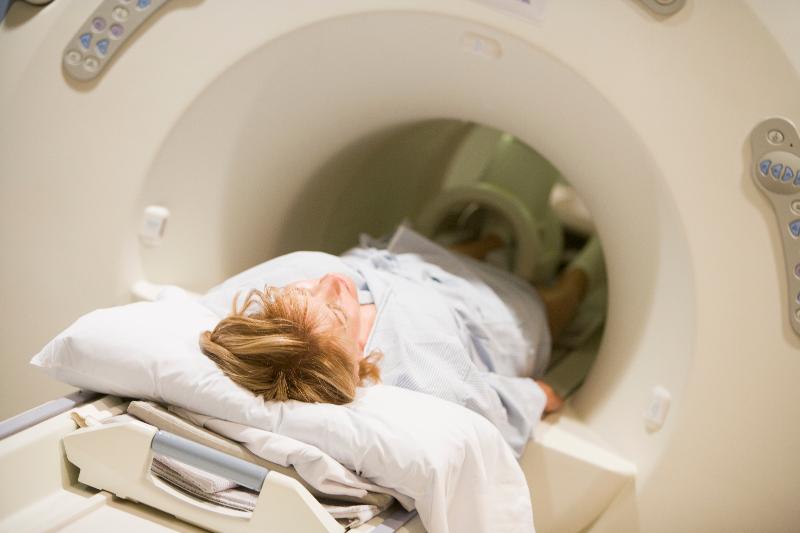
Magnetic Resonance Imaging

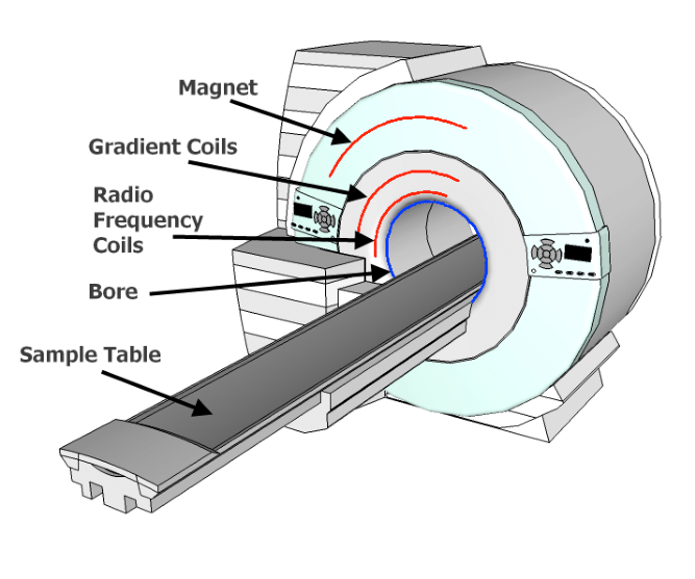
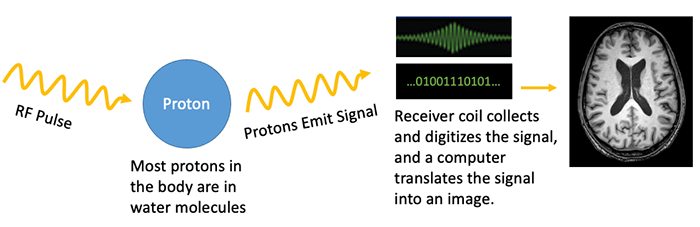
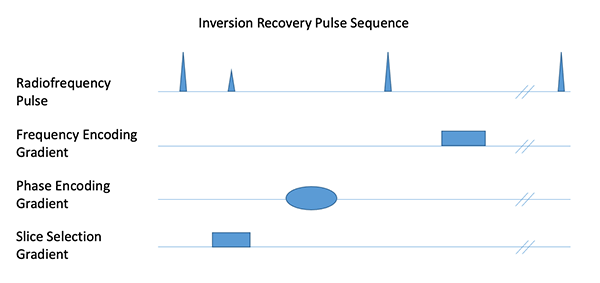
|
|
T2 Weighted Imaging (T2) |
|
|
T1 with Fat Saturation (T1 fat-sat) |
T2 with Fat Saturation (T2 fat-sat) |
|
|
Fluid Suppression (FLAIR) |
Diffusion Weighted Imaging (DWI |
|
|
Susceptibility Weighted Imaging (SWI) |
Proton Density |
T1 with IV Gadolinium Contrast (T1-post) |
|
Fluid represented in a T1 and T2 weighted image |
|
|
|
|
|
T1: Dark |
T2: Bright |
|
Fat represented in a T1 and T2 weighted image |
|
|
|
|
|
T1: Bright |
T2: Dark |
|
Muscle represented in a T1 and T2 weighted image. |
|
|
|
|
|
T1: Isointense |
T2: Isointens |
|
White matter represented in a T1 and T2 weighted image |
|
|
|
|
|
T1: Isointense |
T2: Isointense |
|
Signal intensity (brightness) is often described as relative signal intensity. For example:
|
|
 Signal intensity (brightness) is often described as relative signal intensity. For example:
Signal intensity (brightness) is often described as relative signal intensity. For example:
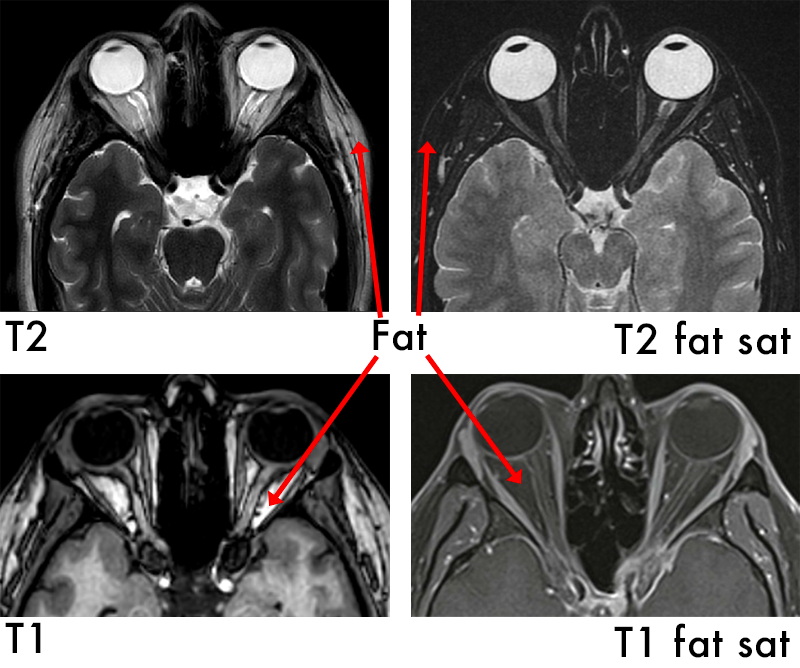
Fat saturation is an additional technique that can be added on to any sequence
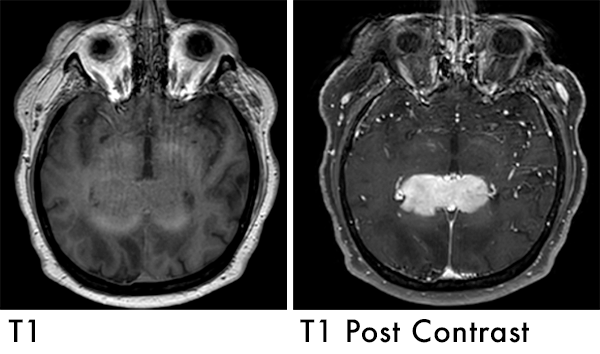
|
Excellent soft tissue contrast (can distinguish between different tissues well) |
|
|
Advanced MRI imaging techniques (fMRI, Cardiac MRI, DTI/Tractography, angiography etc. ) |
|
|
No Radiation (unlike CT and x-ray) |
|
|
MRI can be used to characterize benign and malignant tumors in the abdominal organs. This is a case of multiple hemangiomas (benign vascular masses) in the liver characterized on a T1 post-contrast MRI sequence. |
|
|
MRI can be used to diagnose infections in the bones. |
|
|
MRI is very useful in the diagnosis of ischemic stroke. In acute stroke the movement of water is restricted due to cell swelling and cell membrane dysfunction. DWI is an advanced MRI technique that shows bright signal when the movement of water is restricted and helps detect acute stroke. |
|
|
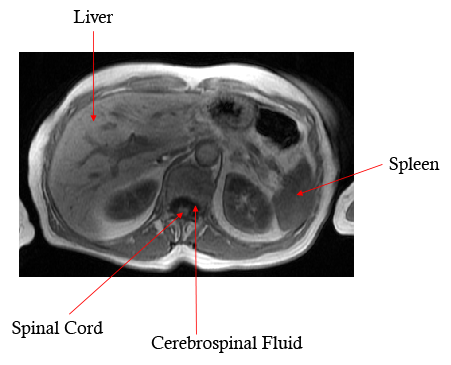
The difference between cerebrospinal fluid and the spinal cord on MRI helps identify cases of spinal cord compression In this case there are metastatic masses in the spinal canal compressing the thoracic spinal cord |
|
|
Cardiac MRI can be used to evaluate the structure of the heart (in this case there is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy) It can also be used to evaluate the function of the heart by taking multiple images during the cardiac cycle The blood perfusion to the heart can be assessed by using special post-contrast MRI techniques |
|
|
MRI is used in the diagnosis of breast cancer. MRI can be used for screening in high risk patients (for example patients with BRCA1 or 2 mutations). MRI can also be used in patients with known breast cancer to look for additional areas of cancer. This is a case of left sided breast cancer. |
|
|
Fetal MRI can be performed to make the diagnosis of congenital or developmental abnormalities prior to delivery. This is a case of twins where twin-twin transfusion syndrome was suspected on prior imaging. This MRI shows normal twin pregnancy. |
|
|
MRI can be used for evaluating vessels. This is a post-contrast MR angiogram showing chronic occlusion of the aorta and proximal iliac arteries. |
|