Economics 172
Spring 2006
Due Friday March 31
Homework 7
Chapter 8
Questions 2, 6, 8, 11, 13
2. It is possible to have the MC curve hitting
the price line at two different output levels.
When the MC is downward sloping and crosses the price line, increasing
output means MC<MR, and the firm should expand
output. When the MC curve is upward
sloping expanding output beyond MC = P (or MR) will reduce profit since
MC>MR.
Using
calculus: Π(q)
= R(q) C(q)
Differentiate with
respect to q: Π(q)
= R(q) C(q) where means first derivative.
Profit
maximization requires Π(q) = R(q) C(q) = 0 or R(q) = C(q)
Now take the
second derivative: Π(q)
= R(q) C(q)
Remember from
calculus that a relative maxium occurs when f(x) < 0 and a relative
minimum is when f(x) >0; that is, the function is at a relative maximum if
the second derivative is negative and a minimum if it is positive.
So if R(q) - C(q) < 0, then profits will be maximized. So when is R(q)
< C(q) ? When the rate of change of
MR is less than the rate of change of MC. When MC crosses MR or price when MC is rising, then R(q) =0 and
C(q) >0.
6. A French government subsidy will not shift
the marginal cost curve since the subsidy is a fixed amount independent of the
output level. It will shift the average
total cost curve downward but not the average variable cost curve. There will now be more cheese produced in the
world than before at any price (the lower costs and higher profits attracts
entry in
The answer to this
problem is similar to Solved Problem 8.3 in the text, except it works in
reverse.
8. If the government passes a law requiring six
months notice before shutting down a plan, that means
that there are fewer short run variable costs for the firm. This increases the firms uncertainty as to
whether it should start producing at all.
Some firms may not enter the market even if there are short run profits
to be earned. Think this is
fanciful? Just look at whats happening
in
11. If
13. Start with the
1. In long run equilibrium, each firm in a perfectly competitive industry earns zero profit. Why would anyone ever want to start a business in a perfectly competitive industry?
If an entrepreneur
thought she could produce the product at lower marginal (and average) costs
than any other competitor, entry would occur because of the attempt to earn
economic profits.
2. The ballpoint pen industry is a competitive industry in long run equilibrium and all pens sell for $2.
a. Assume that all firms have normally shaped average and marginal cost curves. Show, using all relevant graphs the initial long run equilibrium situation for a representative firm in the ballpoint pen industry. Be sure to show output level and all relevant costs.

Ballpoint pens are manufactured in numerous factories all
over the
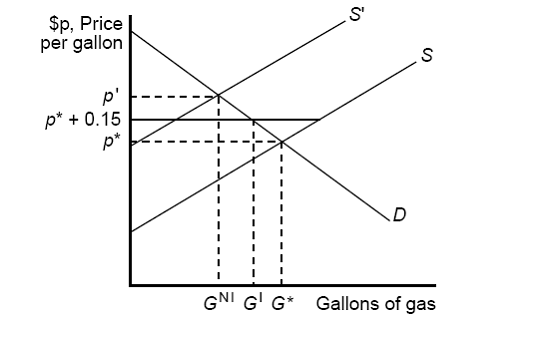
b. Show graphically and briefly discuss how this tax will
affect the market price and quantity of ballpoint pens in the

c. Show and briefly discuss how this tax will affect the price, quantity, and profits of ClevePens in the short run.
Output will fall
from q1 to q2. The price ClevePens can
charge in the market is unchanged because it is in a competitive market. Profits will fall.
d. Show graphically and briefly discuss how this tax will affect the price, quantity, and profits of ClevePens in the long run.
