Community-Engaged Learning Course Designation
Designating a course as Service Learning (SL) or Civic Learning (CL) in the UVM Schedule of Courses conveys to students that there is a community-engaged component to the course; in some departments this fulfills a graduation requirement. Designation also ensures that our institutional data about student learning experiences is accurate. And importantly, designating courses allows CELO to track and reach out to community partners, ensuring open communication and opportunities for feedback, resource-sharing, and future project development.
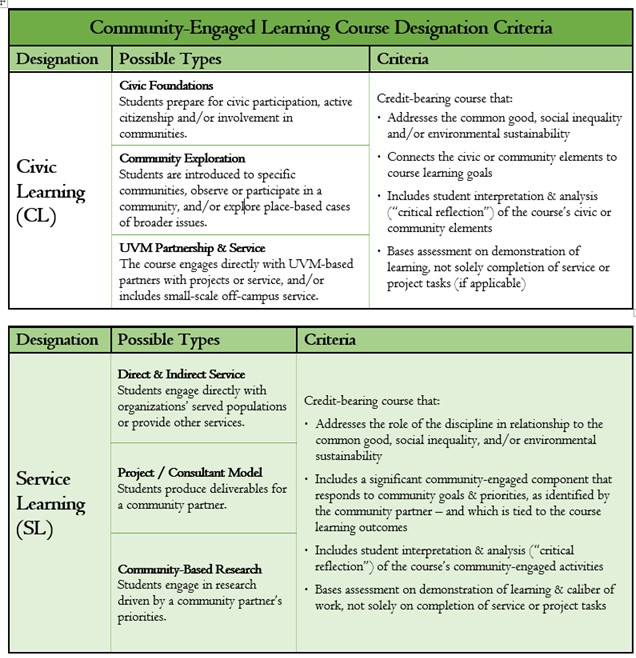
New in FY20, the Civic Learning (CL) designation is appropriate for courses that include many elements of service-learning, but that don't require that student work meets the often-high bar of reciprocity. It is intended to both incentivize and recognize the broad range of community-engaged and preparatory coursework being offered, and we conceived of a number of ways that courses might fulfill the CL designation.
The existing Service Learning (SL) designation has been clarified and made more rigorous: the project or service should be reasonably substantial, and must attempt to meet community needs, as articulated by the community partner.
Community-Engaged Learning Course Designation Criteria
UVM follows a pedagogical model of community-engaged learning, rather than an “hours of service” model. This means that designation is based on criteria related to best practices in community engagement, academic rigor and reciprocity, rather than by counting hours. Courses qualify for designation when the community-engaged learning is constructed so as to deepen student learning while benefitting a community partner, regardless of the scale, scope or duration of the project or service.
(Download the below criteria as a Word document.)
Why Use Community-Engaged Learning Pedagogy?
CELO assists UVM faculty in developing the community-engaged learning components of their courses, in line with their intended learning goals. Faculty may choose community-engaged learning pedagogy in courses for many reasons, including, but not limited to:
- Providing applied or integrative opportunities for students
- Contributing the skills of their discipline to social change efforts or for the public good
- Connecting research and community engagement through teaching
- Connecting students with places, people or institutions to deepen their learning or capacity to act as engaged citizens and community members

