PBIO 109 - 2011

Asteraceae
arcuate veins
AP Airport Park 6/29
BNA
Beach at end of North Ave
6/28
CW Centennial Woods 6/21
EAH Ethan Allen Homestead
6/24
EAP Ethan Allen Park
6/27
LCC Lake Champlain Canoe
OL Oakledge
RR
Red Rocks
7/14
SB Shelburne Bay
UVM1 6/20 (beyond the parking lot)
UVM2 6/22 (in the commuter lot area)
UVM3
7/5 (around Stafford)

Asteraceae
leaf design pinnate; leaf dissection compound
REVISIT: June 22, UVM2
strong odor of crushed leaves characterizes one tribe of Asteraceae

Leguminosae (Fabaceae)
pinnately compound leaves

Labiatae (Lamiaceae)
leaves opposite, simple, palmate
square stems
pungent odor of crushed foliage = essential oils

Apocynaceae
opposite leaves, white latex --- two characters define one family in Vermont

Gramineae (Poaceae)
MONOCOT LEAF FEATURES:
no midvein, parallel secondaries, POACEAE FEATURE: sheathing leaf

Urticaceae
opposite leaves with serrate edges, strong bark
stipules (four per node)

Rosaceae
~alternate, palmately compound leaves, leaflets with pinnate venation;
~canes last two years, flower the second,
~stipules characteristic of Rosaceae, see #3

Rosaceae
~introduction to odor of crushed leaves --- here an almond odor characteristic of cyanide
~stipules characteristic of Rosaceae, like #2

Cornaceae
~arcuate secondary veins, tertiary veins perpendicular to midrib
~sympodial branching (constant surrender of dominance)

Balsaminaceae
~annual
~crenate leaves

Rhamnaceae
~indecisive leaves (vary from alternate to opposite with position on shoot)
~SHARP THINGS: shoot-tip transformed into thorn

Berberidaceae
~SHARP THINGS: leaf transformed into spine

Rosaceae
~SHARP THINGS: stipules transformed into spines

9. corn salad/ valerian Valeriana
Valerianaceae
~opposite, compound leaves
~medicinal value is as sedative. MISREPRESENTED IN THE FIELD. See http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S009130570300368X

Leguminosae (Fabaceae)
~SHARP THINGS: even better spines transformed from stipules
~FAMILY CHARACTERS: alternate, compound leaves and stipules

Caryophyllaceae
~flowers imperfect (one sex missing), plants diecious (have one or the other kind of flower, not both)
~FAMILY CHARACTERS: opposite leaves, swollen nodes

Labiatae (Lamiaceae)
~five fusesd petals, bilateral symmetry
~calyx (largely hidden in this picture) five sepals, radially symmetrical

Leguminosae (Fabaceae)
~FLOWER STRUCTURE: 5 fused sepals, corolla of five petals, bilaterally symmetrical --- petals are one banner, two wings making a balloon, and two fused keels making a sort of long curved cone enclosing the stamens

Crassulaceae
~five simple pistils
~stamens twice the petals
~succulent leaves
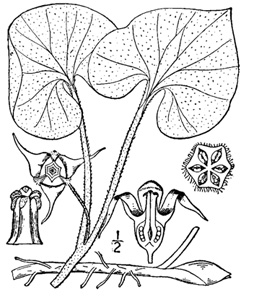
Aristolochiaceae
~essential oils of the magnoliids
~three sepals
~ fruits splitting into six sections
~each with seeds with arils for ant dispersal

Papaveraceae
~colored latex

Leguminosae
FAMILY CHARACTERS
~alternate, compound leaves
~stipules
~bilaterally symmetrical flowers with
~imbricate petals --- banner is outside of wings and keels

Rubiaceae
0 sepals
4 connate petals
4 stamens adnate to the petals
2 pistils, only the ovary fused, ovary inferior

Rosaceae
5 separate sepals and petals
many stamens
many simple pistils, superior ovaries

Papaveraceae
alternate, pinnately compound leaves
2 deciduous sepals
4 separate petals, radial symmetry
many stamens
one pistil splitting into two vales (the green canoes) and two placentae (the hoop) bearing seeds with arils
ovary superior (perianth scars at ovary base)

~dioecious plants
~from the fruit: five pistils with connate ovaries; the compound ovary is inferior (perianth scars at ovary summit)
In this picture, most of the fruits have turned blue with further ripening.

Labiatae (Lamiaceae)
NOTE WRONG COMMON NAME IN THE FIELD.
~FAMILY: square stems, opposite leaves, flowers with connate bilaterally symmetrical corollas, adnate stamens fewer than the perianth parts, and a superior ovary
There are two petals in the upper and three petals in the lower lip.
Wikipedia: "uterine tonic and prevention of uterine infection in women, hence the name Motherwort"

Caryophyllaceae
FAMILY: opposite leaves, swollen nodes, and stamens twice the petals
The current name of this plant is Silene vulgaris. Silene cucubalus is a correct but old name.
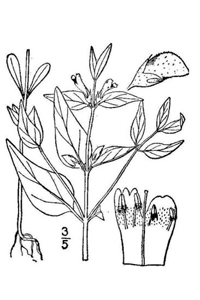
Scrophulariaceae (Orobanchaceae according to APG)
ASTERID CHARACTERS
~connate corolla
~stamens = or < petals
~stamens adnate to the corolla

Leguminosae (Fabaceae)
~precise placement of pollen
NEW FAMILY CHARACTERS:
~stamens twice the petals
~stamens connate (9/10)
~one simple pistil

Compositae (Asteraceae)
~yellow ray flowers
~black disk flowers
~blossom is a head inflorescence

marginal
- pea (Pisum, Leguminosae)
axile
- okra (Abelmoschus, Malvaceae)
parietal
- papaya (Carica, Caricaceae)
- melon (Cucumis, Cucurbitaceae)
axile and parietal
- bell pepper (Solanum, Solanaceae)

berries
- tomato (Lycopersicon, Solanaceae)
- avocado (Persea, Lauraceae)
drupes
- nectarine (Prunus, Rosaceae)
- cherry (Prunus, Rosaceae)
- date (Phoenix, Palmae)
drupes in clusters
- raspberry (Rubus)

fleshy hairs in locules - orange (Citrus, Rutaceae)
fleshy hypanthium - apple (Malus, Rosaceae)
fleshy receptacle - strawberry (Fragaria, Rosaceae)
fleshy inflorescence - pineapple (Ananas, Bromeliaceae)
fleshy placenta - banana
(Musa, Musaceae)

(Cocos, Palmae)

Labiatae
a bumblebee flower - blue-purple with a landing and nectar hidden deep in the flower, no odor

Scrophulariaceae
outcrossing promoted by
~stamens opening first in each flower
!indeterminate inflorescence means lower flowers (old) are female, upper flowers (young) are male.
~bees fly up, encountering pollen up high and then flying to a new plant and starting at the bottom in the femaile flowers.

Caprifoliaceae
FAMILY CHARACTERS
~ opposite leaves, no stipules
~ connate corolla, stamens equal to or fewer than corolla lobes, inferior ovary
hummingbird syndrome includes:
red color, abundant nectar, no landing place, nectar deep in tube


Onagraceae
FAMILY CHARACTERS
~4 sepals,
~4 separate petals
~stamens twice the petals
~hypanthium
~inferior ovary (of four fused carpels)
Sphinx moth syndrome: long tube, abundant nectar, landing, weak color, strong pleasant scent


old Liliaceae, now Hemerocallidaceae or Xanthorrhoeaceae
monocot features:
~two whorls of three tepals
~parallel secondary veins


Arisaema, Araceae
FAMILY CHARACTERS:
~spathe and spadix
left: triphyllum
right: stewardsonii (note leaflets don't look right for stewrdsonii) but spathe does

Ranunculaceae
FAMILY CHARACTERS:
~palmate leaf design
~leaves lobed or compound
~no fusion in flower
~stamens many

Apocynaceae
FAMILY CHARACTERS
~opposite, simple leaves
~ white latex
~the asterid trio (connate corolla, stamens adnate to the corolla, stamens = or < corolla parts)
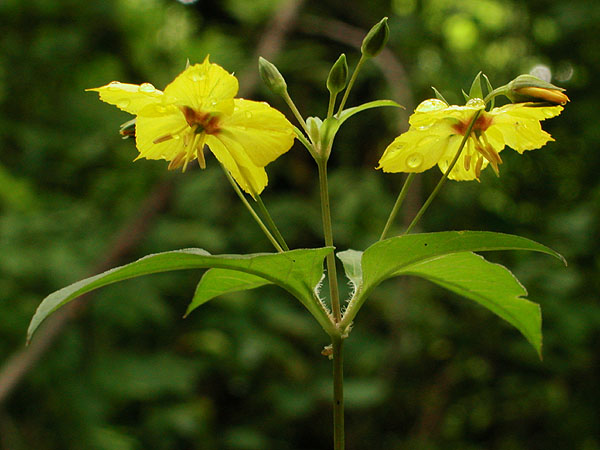

Primulaceae
FAMILY CHARACTERS
~stamens same number as and opposite the petals
~stamens adnate to the petals
corolla connate
~vegetative: opposite, simple leaves
an Asterid "wannabe"
*sweetflag, Acorus, Acoraceae
*arrowleaf, Sagittaria, Alismataceae
*calla lily Calla Araceae
*duckweeds Lemna and Wolffia, Araceae
*sedges, Scirpus, Carex Cyperaceae
*cattail, Typha Typhaceae

FAMILY CHARACTERS
~inferior ovary
~hypanthium
~separate petals
ANOMALOUS CHARACTERS
~flower parts not in fours
This is a hoverfly flower ---- the pollination syndrome drove the number change.

PRIMITIVE CHARACTERS
~undifferentiated perianth
~stame-perianth transitional structures
~many stamens
SPECIALIZED CHARACTERS
~connate gynoecium
~laminar stamens (for bettel pollination)


Cruciferae (Brassicaceae)
FAMILY CHARACTERS:
~stamens 6 (4 long and 2 short) --- that is the stamens are more than the the petals, but not twice as many
~petals and sepals both 4, unfused

Sarraceniaceae
bumblebee pollinated, petals still in place in this photo
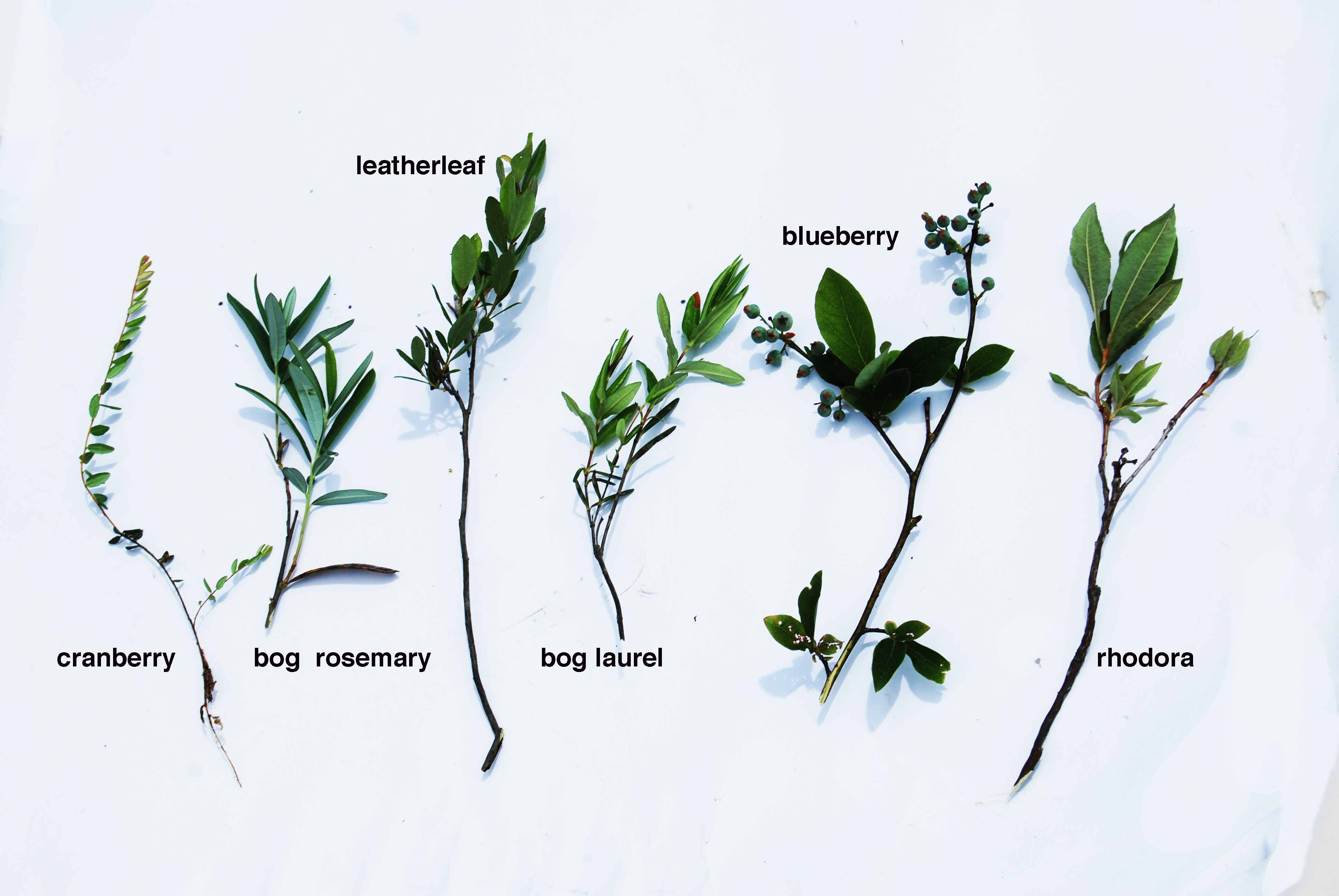

cranberry (Vaccinium)
bog rosemary (Andromeda)
leatherleaf (Chamaedaphne)
bog laurel (Kalmia)
high-bush blueberry (Vaccinium)
rhodora (Rhododendron)

Cistaceae
endangered in Vermont -- a remnant of the shifting-sand flora along glacial Lake Champlain

Phrymaceae
much like a mint, but no mint essential oils and ovary with one ovule in one locule instead of four in two locules
~passive animal dispersal, hooks are sepal tips
Eastern North American -- Eastern Asian disjunction inffered to be fmor vicariance

Asteraceae
REVIEW OF FAMILY CHARACTERS
~connate corolla
~connate anthers
~modified calyx (called a pappus)
~inferior ovary
SPECIAL FEATURES
~all ray flowers, no disc flowers

Rosaceae
ROSACEAE CHARACTERS
~alternate leaves with stipules
~many stamens
~ (hypanthium not evident)
~passive animal dispersal, hooks are hairs on hypanthium
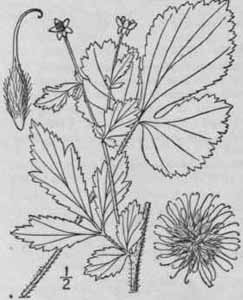
Rosaceae
~passive animal dispersal, hooks are stigmas

FAMILY CHARACTERS
~radial symmetry
~superior ovary
asterid trio
~connate corolla
~stamens = petals
~stamens adnate to petals
SPECIAL FEATURE
~poricidal stamens

Campanulaceae
FAMILY CHARACTERS
~alternate leaves
~latex
~inferior ovary
~connate corolla (asterid)
~stamens = petals (asterid)
~stamesn not adnate (not asterid)
~carpels three (rare in asterids, 2 is typical)

Rubiaceae
FAMILY CHARACTERS
~opposite leaves
~stipules
~inferior ovary
~radial symmetry
ASTERID CHARACTERS
~connate corolla
~adnate stamens
~stamens = petals
~two-carpellate
HETEROSTYLY: long-styled and short-styled flowers always on different plants

FAMILY CHARACTERS
~compound leaves
~expanded petiole base
~celery essential oil
~separate petals
~stamens = petals
~ovary inferior